
Gall Stone Removal
Gall Stone Removal
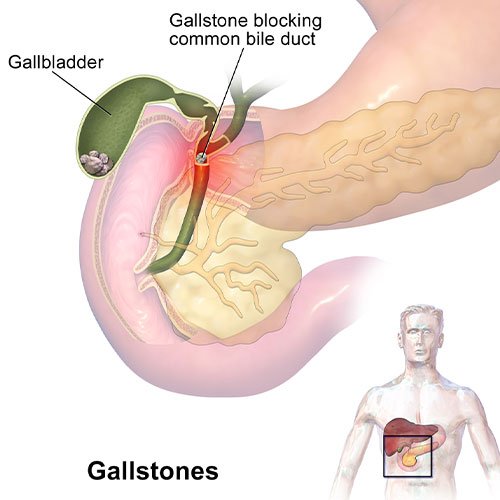
Gallstone removal, medically known as cholecystectomy, is a procedure aimed at eliminating gallstones that form in the gallbladder. Gallstones are solid particles that develop due to imbalances in the substances that make up bile, such as cholesterol and bilirubin. These stones can cause significant discomfort, pain, and even severe health complications if they obstruct the bile duct or cause gallbladder inflammation (cholecystitis).
Post-surgery, patients are typically advised to rest and gradually return to regular activities over a few days to weeks, depending on the surgery type. A low-fat diet is often recommended to ease the transition since bile is no longer stored in the gallbladder for timed release.
Types of Gallstone Removal Procedures
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy (Minimally Invasive Surgery)
- This is the most common approach for gallstone removal. Surgeons make small incisions in the abdomen and insert a laparoscope (a small camera) along with specialized surgical tools to remove the gallbladder.
- This method is less invasive, leading to quicker recovery times, minimal scarring, and less postoperative pain.
Open Cholecystectomy
- In cases where laparoscopic surgery isn’t feasible due to severe inflammation, scarring, or other complications, an open cholecystectomy may be performed.
- A larger incision is made in the abdomen to directly access and remove the gallbladder.
- Recovery is generally longer compared to laparoscopic surgery.
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
- ERCP is used when gallstones are lodged in the bile ducts rather than in the gallbladder itself.
- A flexible endoscope is inserted through the mouth, down the digestive tract, and into the bile duct to retrieve the stones or place a stent to relieve the obstruction.
Oral Dissolution Therapy (Non-surgical)
- For patients who cannot undergo surgery, certain medications may be prescribed to dissolve cholesterol-based gallstones.
- This method is rare and may take months or even years to achieve results, depending on the stone size and composition.
