
Fibroids Removal
Fibroids Removal
Fibroids, also known as uterine leiomyomas or myomas, are non-cancerous growths that develop in or on the uterus. They can vary in size and may cause a range of symptoms, depending on their location, size, and number. Some common symptoms include heavy menstrual bleeding, prolonged periods, pelvic pain or pressure, frequent urination, and complications during pregnancy and labor.
Recovery times vary based on the treatment approach. Minimally invasive procedures typically require less downtime compared to major surgery. After treatment, regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor recovery and check for any recurrence of fibroids.
While fibroids are common, effective treatment options are available. Women experiencing symptoms should consult with a healthcare provider to discuss their options based on individual circumstances and treatment goals. Early diagnosis and appropriate management can significantly improve quality of life and reproductive health.
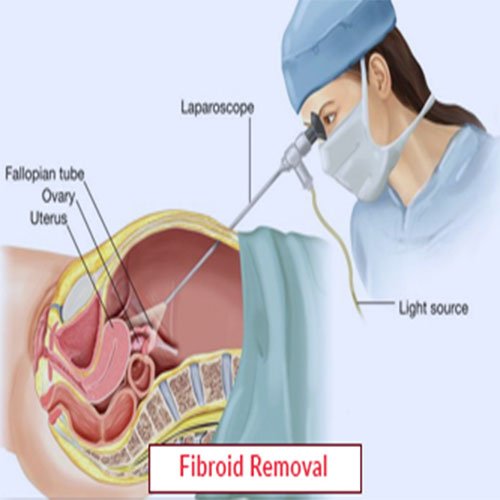
Types of Fibroids
- Intramural Fibroids: These grow within the uterine wall and are the most common type.
- Subserosal Fibroids: These protrude outside the uterus and can cause pressure on nearby organs.
- Submucosal Fibroids: These develop just beneath the lining of the uterus and can lead to heavy bleeding.
- Pedunculated Fibroids: These are attached to the uterus by a stalk and can be either subserosal or submucosal.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis typically involves a thorough medical history and pelvic examination. Imaging tests, such as ultrasound, MRI, or hysterosalpingography, may be used to confirm the presence of fibroids.
