
Gynaecomastia
Gynaecomastia
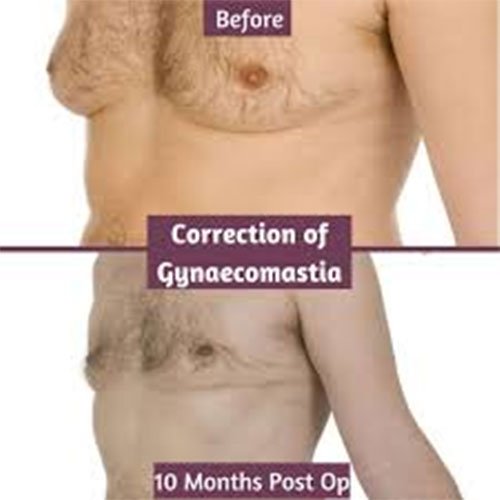
Gynecomastia is a medical condition characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in males. It can occur in one or both breasts and is often the result of an imbalance between the levels of testosterone and estrogen in the body. While gynecomastia is typically benign, it can lead to psychological distress and body image issues for those affected.
While gynecomastia is a common condition and often harmless, it can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Individuals experiencing symptoms should consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and potential treatment options.
Causes
Gynecomastia can be caused by various factors, including:
- Hormonal Changes: Puberty, aging, and hormonal imbalances can lead to increased estrogen levels or decreased testosterone levels.
- Medications: Certain medications, including anti-androgens, anabolic steroids, anti-anxiety medications, and some heart and ulcer drugs, can contribute to gynecomastia.
- Health Conditions: Conditions such as liver disease, kidney disease, hyperthyroidism, and tumors affecting the testes can alter hormone levels and lead to breast tissue growth.
- Substance Use: Alcohol, marijuana, and certain recreational drugs can influence hormonal balance and contribute to the development of gynecomastia.
- Genetics: Genetic conditions, such as Klinefelter syndrome, can predispose individuals to gynecomastia.
Symptoms
The primary symptom of gynecomastia is swollen breast tissue, which may be tender or painful. Other symptoms can include:
- A rubbery or firm mass of glandular tissue located under the nipple.
- Discomfort or sensitivity in the breast area.
- In some cases, an increase in breast size may be noticeable.
