
Male Breast
Male Breast
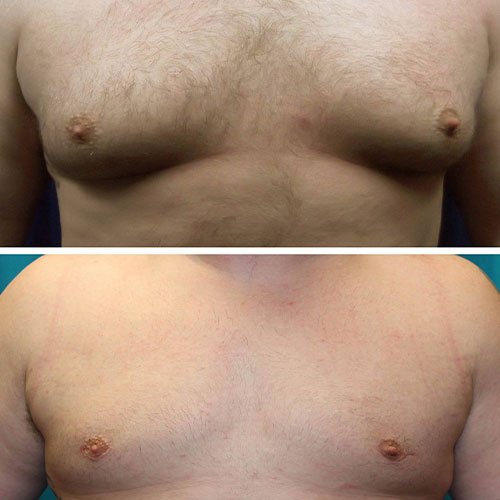
Male breast issues can include a variety of conditions, with the most common being gynecomastia, which is the enlargement of breast tissue in males. Here’s an overview of the male breast and the associated treatment options:
While male breast conditions can range from benign to serious, there are effective treatment options available. It is important for individuals experiencing symptoms to consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management. Early intervention can lead to better outcomes, especially in cases of male breast cancer.
Male Breast Anatomy
Males have breast tissue similar to females, but it is typically less developed. The male breast consists of:
- Glandular Tissue: This is the breast tissue that can develop under certain conditions.
- Adipose Tissue: Fatty tissue that surrounds the glandular tissue.
- Ducts: These can carry fluid but are usually undeveloped in males.
Common Conditions
Gynecomastia: This condition is characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in males. It can be caused by hormonal imbalances, certain medications, obesity, and other factors. Symptoms include swollen breast tissue, tenderness, and, in some cases, pain.
Male Breast Cancer: Although rare, men can develop breast cancer. Risk factors include age, family history of breast cancer, genetic mutations (such as BRCA2), and exposure to radiation. Symptoms may include a lump in the breast, changes in the nipple or breast skin, and discharge.
Pseudogynecomastia: This is not true gynecomastia but rather an accumulation of fat in the breast area, often related to obesity. It is more common in overweight individuals.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of male breast conditions typically involves:
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will examine the breast tissue.
- Imaging Tests: Mammograms or ultrasounds may be used to evaluate the breast tissue.
- Biopsy: In cases of suspected breast cancer, a biopsy may be performed to analyze the tissue.
Treatment Options
Gynecomastia:
- Observation: If the condition is mild and not causing discomfort, a healthcare provider may recommend monitoring it.
- Medications: In some cases, hormonal treatments may help balance hormone levels. Options include anti-estrogens like tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors.
- Surgery: For more severe cases, surgical options include liposuction (to remove excess fat) or mastectomy (to remove glandular tissue).
Male Breast Cancer:
- Surgery: This often involves removing the tumor and surrounding tissue (lumpectomy) or mastectomy.
- Radiation Therapy: Post-surgery, radiation may be used to eliminate any remaining cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: This may be recommended depending on the stage of cancer and other factors.
- Hormone Therapy: For hormone-sensitive cancers, medications that block hormones may be utilized.
Pseudogynecomastia:
- Weight Loss: Addressing obesity through diet and exercise may help reduce the appearance of breast tissue.
- Liposuction: This can also be an option for fat removal.
